Yet Another Tree Problem
Nayra doesn't like stories of people receiving random trees as birthday presents, but this time she received a tree as a present for her own birthday! After struggling for a day trying to figure out what to do with this tree, she asked Aryan for help. He gave her this problem.
You are given a tree with vertices and weighted edges. It is rooted at vertex .
Define to be the maximum weight of an edge on the shortest path between vertex and vertex in this tree.
Just calculating is too easy, so you have to process queries.
In each query, you are given distinct vertices . You have to compute the sum of the -values of each pair of vertices among these , i.e, the value
Note: The input and output are large, so use fast input-output methods.
Input Format
- The first line of input contains a single integer denoting the number of test cases. The description of test cases follows.
- The first line of each test case contains two space-separated integers and , denoting the number of vertices in the tree and the number of queries respectively.
- The second line contains space-separated integers , where is the parent of vertex .
- The third line contains space-separated integers , where is the weight of the edge between vertices and .
- The next lines contain queries you will have to answer. The description of queries follows.
- The -th line contains an integer followed by distinct space-separated integers , where is the number of vertices in this query and denote the vertices themselves.
Output Format
For each test, print one line containing space-separated integers. The -th of these integers should be the answer to the -th query.
Constraints
- All present in a single query are distinct
- It is guaranteed that the sum of over all queries over all test cases in a single test file does not exceed
- It is guaranteed that the sum of over all test cases in a single test file does not exceed
Sample Input 1
1
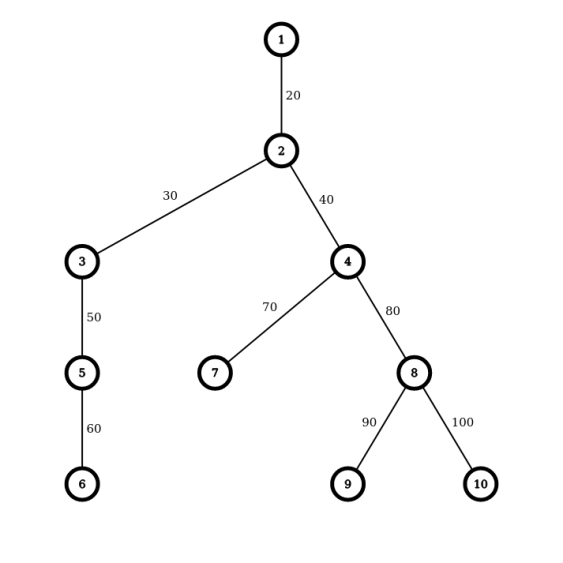
10 1
1 2 2 3 5 4 4 8 8
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10 1 4 5 6 2 3 7 8 9 10
Sample Output 1
3300
Sample Input 2
1
10 2
1 2 2 3 5 4 4 8 8
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
4 1 4 5 6
4 2 3 7 8
Sample Output 2
320 410
Explanation
In the second sample:
Let's look at different values of for this tree.
For the first query, , , , , , . The sum of all these values is .
For the second query, , , , , , . The sum of all these values is .
Note: The second sample does not satisfy the constraint , so it won't be present in the actual test data. It's added here only for illustration.



Comments
Post a Comment